Aging might feel unstoppable, but cutting-edge research shows you can actually slow down and even reverse many aging processes at the cellular level. This guide is for health-conscious adults who want to go beyond basic anti-aging advice and discover what science really says about turning back your biological clock.
We’ll explore the cellular mechanisms that drive aging and why understanding them gives you real power to fight back. You’ll discover proven nutrition strategies that protect your DNA and boost cellular repair, plus exercise protocols that can literally make your body younger on a biological level. We’ll also dive into how optimizing your sleep and managing stress can dramatically slow aging, along with the latest supplements and therapies showing real promise in longevity research.
Ready to learn how to reverse aging using evidence-based strategies that actually work? Let’s break down the science and give you practical tools to help your body age in reverse.
Understanding the Science Behind Cellular Aging
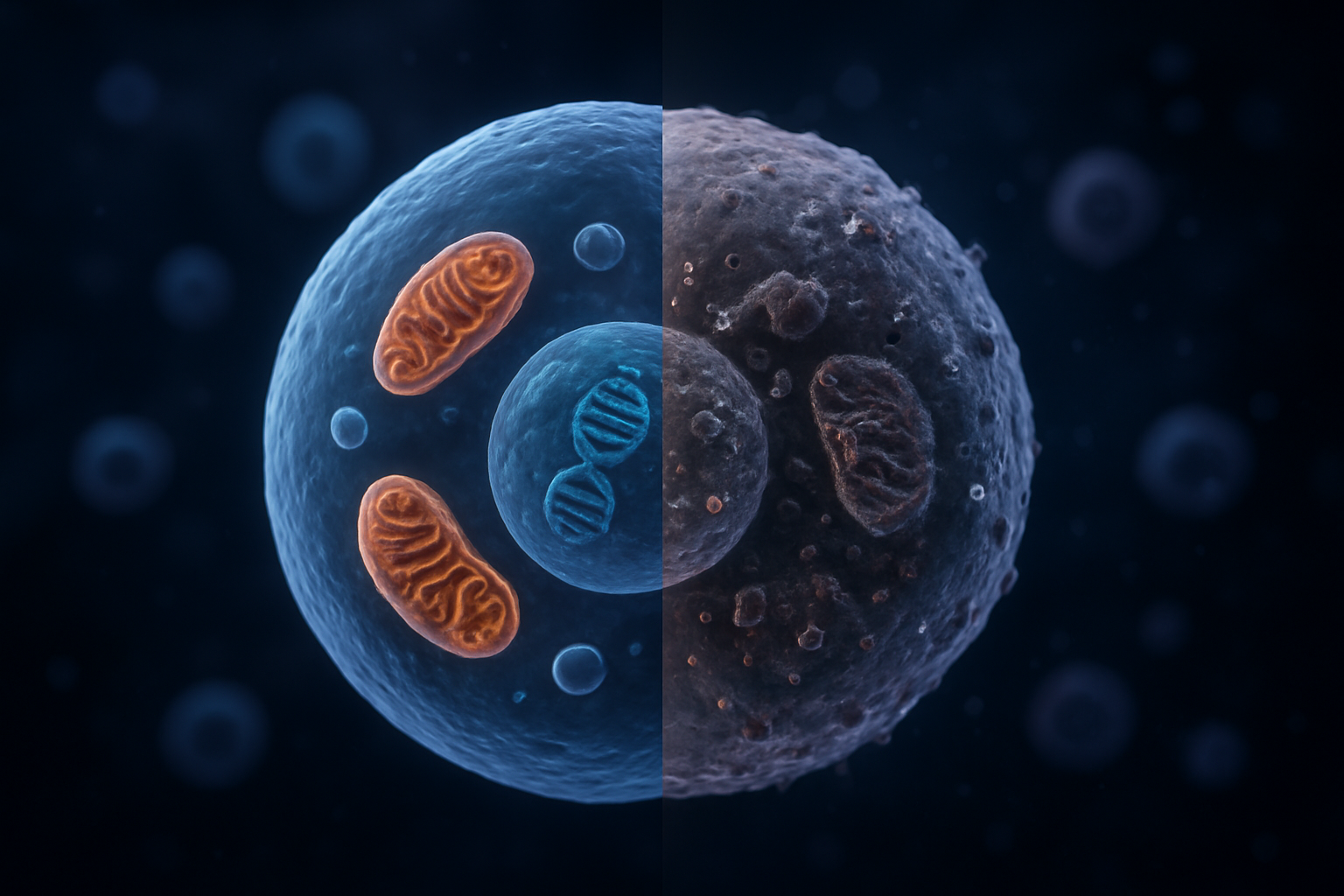
Telomere Shortening and DNA Damage Mechanisms
Think of telomeres as the plastic caps on shoelaces – they protect the ends of your chromosomes from fraying and damage. Every time your cells divide, these protective caps get slightly shorter. Once they become critically short, your cells enter senescence or die, which directly contributes to aging.
DNA damage happens constantly in your body through normal metabolic processes and external factors like UV radiation. Your cells have repair mechanisms, but they become less efficient over time. This accumulated damage leads to mutations, cellular dysfunction, and eventually contributes to age-related diseases.
Key telomere shortening factors:
- Chronic stress and cortisol elevation
- Poor diet high in processed foods
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Environmental toxins
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Energy Decline
Your mitochondria are cellular powerhouses that produce ATP, the energy currency your body runs on. As you age, these organelles become damaged and less efficient, leading to decreased energy production and increased oxidative stress.
Mitochondrial DNA is particularly vulnerable to damage because it lacks the protective histones found in nuclear DNA. This damage accumulates over time, creating a vicious cycle where damaged mitochondria produce more reactive oxygen species, causing further damage to nearby cellular components.
Signs of mitochondrial dysfunction:
- Chronic fatigue and reduced stamina
- Muscle weakness and poor recovery
- Brain fog and cognitive decline
- Increased susceptibility to illness
- Poor temperature regulation
Protein Misfolding and Cellular Waste Accumulation
Proteins are workhorses of your cells, but they can become damaged or misfold due to oxidative stress, heat, or genetic errors. When proteins misfold, they often clump together forming aggregates that interfere with normal cellular function.
Your cells have quality control systems called chaperones and the ubiquitin-proteasome system that help refold damaged proteins or mark them for destruction. However, these systems become overwhelmed with age, leading to accumulation of cellular junk.
Common protein aggregates in aging:
- Beta-amyloid plaques (Alzheimer’s disease)
- Tau tangles (neurodegeneration)
- Lipofuscin (age pigment)
- Advanced glycation end products (AGEs)
Hormonal Changes That Accelerate Aging
Your endocrine system orchestrates countless biological processes, but hormone production naturally declines with age. This decline affects everything from metabolism and muscle mass to cognitive function and immune response.
Growth hormone and IGF-1 levels drop significantly after age 30, affecting tissue repair and regeneration. Sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen also decline, impacting bone density, muscle mass, and cardiovascular health. Thyroid function often decreases, slowing metabolism and energy production.
Major hormonal changes with age:
| Hormone | Change | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Hormone | 14% decrease per decade after 30 | Reduced muscle mass, slower healing |
| Testosterone | 1-2% decline annually after 40 | Loss of muscle, bone density, libido |
| Estrogen | Sharp decline during menopause | Bone loss, cardiovascular changes |
| Thyroid | Gradual decrease in T3/T4 | Slower metabolism, fatigue |
| Melatonin | 50% reduction by age 50 | Sleep disruption, reduced antioxidant protection |
Nutrition Strategies to Combat Aging at the Cellular Level

Caloric Restriction and Intermittent Fasting Benefits
Reducing caloric intake by 10-30% while maintaining adequate nutrition triggers powerful cellular repair mechanisms that can dramatically slow aging. Your cells respond to this controlled stress by activating autophagy – essentially a cellular housekeeping process that removes damaged proteins and organelles while recycling their components.
Studies show that people who practice caloric restriction experience improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation markers, and increased production of NAD+, a crucial molecule for cellular energy and DNA repair. The most impressive results come from combining moderate caloric restriction with intermittent fasting protocols.
Time-restricted eating windows create metabolic flexibility, allowing your body to switch between glucose and fat burning more efficiently. Popular approaches include:
- 16:8 method: Fast for 16 hours, eat within 8 hours
- 5:2 approach: Normal eating 5 days, 500-600 calories 2 days
- Alternate day fasting: Rotating between normal and very low-calorie days
Research from the University of Southern California demonstrates that even 72-hour fasts can regenerate immune cells and clear out damaged ones. The key lies in the cellular stress response – your body becomes more resilient and efficient when faced with controlled periods of nutrient scarcity.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Protect Against Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation accelerates aging by damaging cellular structures and promoting tissue breakdown. Your diet can either fuel this inflammatory fire or provide powerful compounds that extinguish it before damage occurs.
Omega-3 fatty acids from wild-caught fish, walnuts, and flax seeds directly reduce inflammatory cytokines while supporting cellular membrane integrity. Aim for at least 2-3 servings of fatty fish weekly or consider algae-based supplements for vegetarians.
Polyphenol-rich foods act like cellular bodyguards, neutralizing free radicals before they can damage DNA and proteins. The most potent sources include:
| Food Category | Top Sources | Key Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| Berries | Blueberries, elderberries, acai | Anthocyanins, resveratrol |
| Vegetables | Broccoli, spinach, kale | Sulforaphane, quercetin |
| Spices | Turmeric, ginger, cinnamon | Curcumin, gingerol |
| Beverages | Green tea, coffee | EGCG, chlorogenic acid |
Curcumin deserves special attention – this golden compound from turmeric crosses the blood-brain barrier and reduces neuroinflammation while boosting brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Pair it with black pepper to increase absorption by 2000%.
Dark leafy greens provide folate and nitrates that support cellular energy production while reducing oxidative stress. Raw garlic contains allicin, which protects against DNA damage and supports immune function.
Essential Nutrients for DNA Repair and Cellular Regeneration
Your cells constantly repair DNA damage from environmental toxins, UV radiation, and normal metabolic processes. Specific nutrients serve as cofactors for enzymes involved in this critical maintenance work.
B-vitamins form the foundation of cellular repair mechanisms. Folate (B9) and B12 support methylation reactions that maintain DNA integrity, while B6 helps produce antioxidant enzymes. Deficiencies in these vitamins accelerate telomere shortening – the protective caps on chromosomes that determine cellular aging.
Vitamin D acts more like a hormone than a vitamin, regulating over 2000 genes involved in immune function and cellular repair. Optimal levels (40-60 ng/mL) support autophagy and reduce cancer risk. Most people need 2000-4000 IU daily, depending on sun exposure and latitude.
Magnesium participates in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including DNA synthesis and repair. This mineral also regulates telomerase activity – the enzyme that rebuilds telomeres. Pumpkin seeds, dark chocolate, and leafy greens provide easily absorbed forms.
Zinc supports immune function and wound healing while protecting against oxidative DNA damage. Oysters contain more zinc per serving than any other food, but grass-fed beef and pumpkin seeds offer excellent alternatives.
Selenium works synergistically with vitamin E to neutralize lipid peroxidation – a process that damages cell membranes. Brazil nuts provide selenium in highly bioavailable forms, but limit intake to 2-3 nuts daily to avoid toxicity.
Vitamin C regenerates other antioxidants and supports collagen synthesis for healthy skin and blood vessels. While citrus fruits get attention, bell peppers, strawberries, and broccoli actually contain higher concentrations per serving.
Exercise Protocols That Reverse Biological Age

High-intensity interval training for mitochondrial health
HIIT stands as one of the most powerful exercise interventions for reversing cellular aging. Your mitochondria—the energy powerhouses within your cells—respond dramatically to short bursts of intense exercise followed by recovery periods. Research shows that HIIT can increase mitochondrial volume by up to 40% and improve their efficiency by 25%.
The magic happens during those demanding intervals when your cells scramble to meet energy demands. This stress triggers mitochondrial biogenesis, essentially forcing your body to create new, more efficient energy factories. A typical protocol involves 30 seconds of all-out effort followed by 90 seconds of active recovery, repeated 6-8 times.
Sprint intervals on a bike, rowing machine bursts, or bodyweight circuits all deliver these benefits. The key is pushing to 85-90% of your maximum heart rate during work periods. Just three HIIT sessions weekly can produce measurable improvements in cellular respiration and energy production within weeks.
Strength training to maintain muscle mass and bone density
Progressive resistance training acts as a fountain of youth for your musculoskeletal system. After age 30, you naturally lose 3-8% of muscle mass per decade, but consistent strength training can completely halt and even reverse this decline.
Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and push-ups stimulate multiple muscle groups while triggering bone-building responses. The mechanical stress from lifting weights signals your bones to increase density and your muscles to synthesize new proteins. This process doesn’t just maintain function—it actively rebuilds what time has worn away.
Weekly Strength Training Framework:
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Sets | Reps | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound lifts | 2-3x/week | 3-4 | 6-12 | 2-3 min |
| Isolation work | 2x/week | 2-3 | 8-15 | 60-90 sec |
| Core stability | 3x/week | 2-3 | 10-20 | 30-60 sec |
Focus on progressive overload—gradually increasing weight, reps, or sets over time. Your muscles and bones need constant challenges to maintain their youth-preserving adaptations.
Flexibility and balance exercises for longevity
Mobility work often gets overlooked, but it’s critical for maintaining independence and preventing the falls that can devastate aging adults. Dynamic stretching before workouts and static stretching afterward keeps joints moving through their full range of motion.
Yoga combines flexibility with balance training while reducing stress hormones that accelerate aging. Regular practice improves proprioception—your body’s awareness of its position in space—which deteriorates with age but responds beautifully to targeted training.
Balance challenges like single-leg stands, heel-to-toe walking, or wobble board exercises strengthen the small stabilizing muscles around your joints. These muscles fire constantly to keep you upright, but they weaken without specific training. Just 10-15 minutes daily of mobility and balance work can prevent years of functional decline.
Daily Mobility Checklist:
- Hip circles and leg swings (2 minutes)
- Shoulder rolls and arm circles (2 minutes)
- Single-leg balance holds (1 minute each leg)
- Deep breathing with gentle spinal twists (3 minutes)
Recovery techniques that optimize cellular repair
Your body performs its most powerful anti-aging work during rest periods between workouts. Active recovery days with light walking or gentle yoga keep blood flowing while allowing repair processes to flourish.
Sleep represents the ultimate recovery tool, but specific techniques can enhance cellular cleanup. Cool-down periods after intense exercise help clear metabolic waste products that would otherwise accumulate and cause inflammation. A 10-15 minute cool-down with light movement and stretching optimizes this clearance.
Contrast showers—alternating between hot and cold water—stimulate circulation and may activate cellular stress response pathways that improve resilience. Start with 30 seconds cold, 90 seconds warm, repeated 3-4 times.
Massage and foam rolling break up fascial restrictions and improve blood flow to recovering tissues. Even 5-10 minutes of self-massage with a tennis ball or foam roller can accelerate recovery and reduce the inflammatory burden that ages your cells prematurely.
The timing of your recovery matters too. Spacing intense workouts 48-72 hours apart gives your cellular repair mechanisms time to work their magic without overwhelming your system’s capacity to adapt and grow stronger.
Sleep Optimization for Maximum Anti-Aging Benefits

Deep Sleep Cycles and Growth Hormone Production
Your body’s most powerful anti-aging mechanism activates while you sleep. During deep sleep stages, particularly slow-wave sleep, your pituitary gland releases up to 75% of your daily growth hormone production. This hormone acts like a cellular repair crew, rebuilding damaged tissues, strengthening bones, and maintaining muscle mass.
The magic happens during the first half of your sleep cycle when you experience the longest periods of deep sleep. Growth hormone surges typically occur every 3-4 hours during sleep, with the most significant release happening within the first 2-3 hours after falling asleep. This timing explains why going to bed early and maintaining consistent sleep schedules can dramatically impact your biological age.
Poor sleep quality directly sabotages growth hormone production. Sleep fragmentation, frequent awakenings, or insufficient deep sleep can reduce growth hormone levels by up to 42% in healthy adults. Age-related decline in deep sleep compounds this problem, creating a vicious cycle where poor sleep accelerates aging, which then further deteriorates sleep quality.
Sleep Duration Requirements for Cellular Restoration
The sweet spot for anti-aging benefits lies between 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Research shows that both sleep deprivation and excessive sleep (over 10 hours) accelerate cellular aging and increase mortality risk.
Different cellular repair processes require varying amounts of time to complete:
- DNA repair: Requires 6-7 hours of sleep
- Protein synthesis: Peaks during 7-8 hours of sleep
- Cellular waste clearance: Needs 7-9 hours for optimal function
- Immune system regeneration: Requires full 8-9 hour cycles
Your brain’s glymphatic system, which clears toxic proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases, becomes 60% more active during sleep. This system needs adequate time to flush out accumulated cellular waste, including amyloid-beta plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Chronic sleep restriction below 6 hours per night shortens telomeres – the protective caps on chromosomes that indicate cellular age. People sleeping less than 6 hours nightly show telomere length equivalent to someone 4-6 years older than their chronological age.
Creating the Ideal Sleep Environment for Recovery
Your bedroom environment directly impacts sleep quality and anti-aging hormone production. Temperature regulation tops the priority list – your core body temperature needs to drop 2-3 degrees Fahrenheit to initiate deep sleep. Keep your bedroom between 60-67°F (15-19°C) for optimal results.
Darkness triggers melatonin production, your body’s natural anti-aging hormone. Melatonin doesn’t just regulate sleep cycles; it acts as a powerful antioxidant protecting cells from oxidative damage. Block all light sources using blackout curtains, eye masks, or covering electronic displays. Even small amounts of light can suppress melatonin by up to 50%.
Essential sleep environment checklist:
- Temperature: 60-67°F (15-19°C)
- Humidity: 30-50% for optimal breathing
- Noise: Under 30 decibels or use white noise
- Lighting: Complete darkness or dim red light only
- Air quality: Proper ventilation and air filtration
- Bedding: Breathable, natural materials
Blue light exposure in the evening disrupts circadian rhythms and delays melatonin release. Stop using electronic devices 2-3 hours before bedtime, or use blue light blocking glasses and apps that filter blue wavelengths after sunset.
Your mattress and pillows directly affect sleep quality and spinal alignment. Replace mattresses every 7-10 years and pillows every 1-2 years to maintain proper support and reduce allergen buildup that can disrupt sleep.
Stress Management Techniques That Slow Aging

Meditation and Mindfulness Practices for Cortisol Reduction
Chronic stress floods your body with cortisol, a hormone that literally ages you from the inside out. When cortisol levels stay high for extended periods, it damages DNA, shortens telomeres, and accelerates cellular aging. Regular meditation acts like a reset button for your stress response system.
Studies show that just 8 weeks of mindfulness meditation can reduce cortisol levels by up to 23%. The key lies in activating your parasympathetic nervous system – your body’s “rest and digest” mode. Start with simple focused breathing for 10-15 minutes daily. Apps like Headspace or Insight Timer can guide beginners through the process.
Effective meditation techniques for cortisol reduction:
- Body scan meditation: Systematically relax each muscle group
- Loving-kindness meditation: Sends positive intentions to yourself and others
- Mantra meditation: Repeating calming phrases like “I am at peace”
- Walking meditation: Combines gentle movement with mindful awareness
Research from Harvard Medical School demonstrates that experienced meditators have significantly longer telomeres compared to non-meditators. Their biological age can be up to 10 years younger than their chronological age.
Breathing Exercises That Activate Longevity Pathways
Your breath is a direct pathway to influencing your autonomic nervous system and cellular health. Specific breathing patterns can trigger the vagus nerve, which activates anti-aging pathways throughout your body.
The 4-7-8 breathing technique stands out for its immediate stress-reducing effects. Inhale for 4 counts, hold for 7, and exhale for 8. This pattern shifts your nervous system into recovery mode within minutes. Practice this before bed or during stressful moments.
Breathing techniques for longevity:
| Technique | Pattern | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Box Breathing | 4-4-4-4 | Balances nervous system |
| Coherent Breathing | 5-5 | Improves heart rate variability |
| Alternate Nostril | Variable | Balances brain hemispheres |
| Bellows Breath | Rapid cycles | Energizes and detoxifies |
Wim Hof breathing combines rapid breathing cycles with breath retention. Research shows this method can influence gene expression related to inflammation and immune function. The controlled stress of breath holding appears to strengthen cellular resilience.
Regular breathwork increases nitric oxide production, which improves blood flow and supports mitochondrial function. These cellular powerhouses become more efficient at producing energy while generating fewer damaging free radicals.
Social Connections and Their Impact on Biological Age
Loneliness literally kills faster than smoking 15 cigarettes daily. The Framingham Heart Study, spanning over 80 years, reveals that strong social connections can extend lifespan by up to 50%. Quality relationships act as a biological buffer against aging.
People with robust social networks show lower levels of inflammatory markers like IL-6 and C-reactive protein. Chronic inflammation accelerates aging across all organ systems. Social support appears to modulate immune function, keeping inflammation in check.
Key elements of age-protective relationships:
- Regular face-to-face interactions (not just digital)
- Emotional support during challenging times
- Shared activities and common interests
- Mutual care and reciprocal relationships
The Blue Zones – regions with exceptional longevity – all emphasize community connection. Residents maintain close family ties and participate in social groups throughout their lives. Their social circles actively support healthy behaviors and provide meaning.
Building new connections at any age benefits biological markers. Volunteer work, joining clubs, or taking classes creates opportunities for meaningful relationships. Even pet ownership provides social benefits, reducing cortisol and blood pressure.
Time Management Strategies to Reduce Chronic Stress
Poor time management creates a constant state of urgency that bathes your cells in stress hormones. Effective time management isn’t about doing more – it’s about reducing the physiological burden of feeling overwhelmed.
Time blocking prevents the scattered attention that triggers cortisol spikes. Assign specific time slots to different activities, including breaks. This creates predictability that calms your nervous system. Your brain stops constantly scanning for the next urgent task.
Anti-aging time management principles:
- Single-tasking: Focus on one activity at a time
- Energy mapping: Schedule demanding tasks during peak energy hours
- Boundary setting: Protect personal time fiercely
- Saying no: Decline commitments that don’t align with priorities
The Pomodoro Technique – working in 25-minute focused bursts followed by 5-minute breaks – naturally aligns with your brain’s attention cycles. This prevents mental fatigue that triggers stress responses.
Regular digital detoxes reduce cortisol production. Constant notifications create micro-stresses that accumulate over time. Designate phone-free hours, especially before sleep. Your nervous system needs uninterrupted recovery periods to perform cellular repair functions.
Planning tomorrow’s priorities before ending today eliminates the mental churning that disrupts sleep. A clear plan signals safety to your subconscious mind, allowing deeper rest and more efficient cellular regeneration.
Cutting-Edge Anti-Aging Supplements and Therapies

NAD+ Boosters and Their Cellular Energy Benefits
NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) serves as the cellular powerhouse behind energy production and DNA repair mechanisms. As we age, NAD+ levels naturally decline by approximately 50% between ages 40 and 60, directly impacting mitochondrial function and cellular repair processes.
Popular NAD+ precursors include nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Clinical studies show these compounds can restore NAD+ levels by 40-60% within weeks of supplementation. Users often report increased energy, improved cognitive function, and better exercise recovery.
Key NAD+ Boosters:
- Nicotinamide Riboside (NR): 300-500mg daily
- Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): 250-500mg daily
- Niacin: Lower cost option, may cause flushing
Research from Harvard Medical School demonstrates that elevated NAD+ levels activate sirtuins – proteins that regulate cellular aging and stress resistance. These “longevity genes” enhance DNA repair, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote healthy mitochondrial biogenesis.
Senolytic Compounds That Eliminate Damaged Cells
Senescent cells accumulate throughout life, secreting inflammatory compounds that accelerate aging and disease. Senolytics represent a breakthrough approach by selectively targeting these “zombie cells” for elimination.
Quercetin combined with dasatinib shows remarkable results in human trials, reducing senescent cell burden by 36% in adipose tissue. Participants experienced improved walking speed, reduced frailty, and decreased inflammatory markers within weeks.
Proven Senolytic Compounds:
- Quercetin + Dasatinib: Gold standard combination
- Fisetin: Natural flavonoid, 20mg/kg body weight
- Navitoclax: Pharmaceutical-grade option
- Piperlongumine: Emerging natural compound
Clinical protocols typically involve intermittent dosing – taking senolytics for 2-3 consecutive days monthly rather than daily supplementation. This approach maximizes senescent cell clearance while minimizing side effects.
Mayo Clinic research reveals that senolytic therapy can extend healthspan by reducing age-related diseases including osteoarthritis, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegeneration. Participants show measurable improvements in physical function and biomarkers of aging.
Peptide Therapies for Tissue Regeneration
Peptides act as cellular messengers, triggering specific regenerative pathways that decline with age. These short chains of amino acids can stimulate growth hormone release, enhance tissue repair, and improve metabolic function.
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound) accelerates healing of tendons, muscles, and gut tissue. Studies show 200-400mcg daily can heal injuries 50% faster than placebo. Athletes and aging adults use BPC-157 to recover from chronic injuries and maintain tissue integrity.
Top Anti-Aging Peptides:
| Peptide | Primary Function | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| BPC-157 | Tissue repair, gut health | 200-400mcg daily |
| GHK-Cu | Collagen synthesis, wound healing | 1-2mg daily |
| Ipamorelin | Growth hormone release | 200-300mcg 2x daily |
| TB-500 | Muscle regeneration | 2-5mg weekly |
| Epithalon | Telomere lengthening | 10mg cycles |
Peptide therapy requires subcutaneous injection for optimal bioavailability. Many users report improved skin quality, faster recovery from workouts, better sleep, and increased lean muscle mass within 4-6 weeks of starting protocols.
Growth hormone releasing peptides like ipamorelin and sermorelin restore youthful hormone patterns without the risks associated with synthetic growth hormone. These compounds naturally stimulate the pituitary gland, maintaining physiological hormone rhythms.
Red Light Therapy and Photobiomodulation Effects
Red and near-infrared light (660-850nm) penetrate skin and stimulate mitochondrial function through photobiomodulation. This non-invasive therapy enhances cellular energy production, reduces inflammation, and accelerates tissue repair at the molecular level.
NASA originally developed LED light therapy for space missions, discovering that specific wavelengths dramatically accelerate wound healing and cell regeneration. Today’s devices deliver therapeutic doses of light that can reverse multiple signs of aging.
Proven Benefits of Red Light Therapy:
- Increases collagen production by 31% (660nm wavelength)
- Reduces fine lines and wrinkles within 12 weeks
- Improves skin elasticity and firmness
- Enhances muscle recovery and reduces soreness
- Supports hair regrowth in pattern baldness
- Reduces joint pain and inflammation
Clinical protocols recommend 10-20 minutes of exposure daily at 6-12 inches from high-quality LED panels. Devices should deliver at least 100mW/cm² power density for therapeutic effects. Many users combine red light with near-infrared (850nm) for deeper tissue penetration.
Research published in Photomedicine and Laser Surgery shows red light therapy increases ATP production by up to 200% in treated cells. This enhanced cellular energy translates to improved healing, reduced oxidative stress, and more youthful cellular function across multiple organ systems.
Environmental Factors That Accelerate or Slow Aging

Toxin exposure reduction strategies
Your environment bombards you with aging accelerators daily. Heavy metals like mercury and lead accumulate in tissues, creating oxidative stress that damages DNA and proteins. Persistent organic pollutants from plastics, pesticides, and industrial chemicals disrupt hormone production and cellular function.
Start with your water source. Install a high-quality carbon block filter that removes chlorine, fluoride, and pharmaceutical residues. Glass storage containers replace plastic ones that leach endocrine disruptors. Choose organic produce when possible, especially for the “Dirty Dozen” fruits and vegetables with highest pesticide loads.
Air quality matters more than you think. Indoor air often contains 2-5 times more pollutants than outdoor air. HEPA air purifiers with activated carbon filters capture particulates and volatile organic compounds. Houseplants like snake plants and peace lilies naturally detoxify your living space.
Personal care products hide toxin sources. Parabens, phthalates, and synthetic fragrances penetrate skin and accumulate over time. Switch to products with recognizable ingredients. Your liver works overtime processing these chemicals instead of performing its anti-aging functions.
Regular sauna sessions support natural detoxification through sweating. Heat shock proteins activated during sauna use protect against cellular damage and extend lifespan. Aim for 15-20 minutes at 160-180°F, 3-4 times weekly.
Blue light protection and circadian rhythm optimization
Blue light wreaks havoc on your internal clock, accelerating aging through circadian disruption. Exposure after sunset suppresses melatonin production by up to 90%, reducing the deep sleep needed for cellular repair and growth hormone release.
Blue light blocking glasses filter harmful wavelengths after 6 PM. Choose amber or red-tinted lenses that block 99% of blue light between 400-490 nanometers. Screen filters and apps reduce exposure, but glasses provide more complete protection.
Natural light exposure during the day strengthens circadian rhythms. Get 10-30 minutes of morning sunlight within two hours of waking. This exposure triggers cortisol production and sets your biological clock for optimal sleep-wake cycles.
Red light therapy offers anti-aging benefits through photobiomodulation. Near-infrared wavelengths (660-850nm) penetrate deep into tissues, stimulating mitochondrial function and collagen production. Use LED panels for 10-20 minutes daily on face and body.
Evening light management creates an aging-protective environment. Dim overhead lights 2-3 hours before bedtime. Use warm-toned bulbs under 3000K color temperature. Salt lamps and candles provide gentle illumination that doesn’t disrupt melatonin synthesis.
Temperature drops naturally signal bedtime. Cool your bedroom to 65-68°F for optimal sleep quality and growth hormone release.
Temperature therapy benefits for longevity
Temperature stress activates powerful longevity pathways through hormesis – the beneficial adaptation to mild stressors. Both heat and cold exposure trigger cellular repair mechanisms that slow aging at the molecular level.
Heat therapy through saunas increases heat shock proteins that protect against protein misfolding and cellular damage. Regular sauna use reduces all-cause mortality by 24% and cardiovascular death by 50% according to Finnish studies. The heat stress mimics exercise benefits, improving heart rate variability and blood vessel function.
Cold exposure activates brown adipose tissue and increases noradrenaline production. Cold showers, ice baths, or cryotherapy sessions boost metabolism and reduce inflammation. Start with 30 seconds of cold water at the end of your shower, gradually building to 2-3 minutes.
Contrast therapy alternates between hot and cold exposure for maximum benefit. Scandinavian traditions of sauna followed by cold plunges optimize circulation and stress hormone balance. This practice strengthens your stress response system, making you more resilient to daily aging factors.
Cold thermogenesis improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Your body burns more calories maintaining temperature, supporting healthy weight management that correlates with longevity. Brown fat activation also releases protective hormones that reduce age-related disease risk.
Time your temperature therapy strategically. Morning cold exposure energizes and improves alertness. Evening heat therapy promotes relaxation and deeper sleep quality.

Turning back your biological clock isn’t about finding a magic fountain of youth – it’s about making smart, science-backed choices every single day. The research is clear: what you eat, how you move, when you sleep, and how you handle stress all play major roles in how quickly or slowly your cells age. From targeting cellular damage with the right nutrients to using exercise as a powerful anti-aging medicine, these strategies work together to help you look and feel younger than your chronological age suggests.
The best part? You don’t need expensive treatments or complicated protocols to get started. Focus on the basics first: eat foods rich in antioxidants, get your heart pumping regularly, prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep, and find healthy ways to manage daily stress. Once you’ve nailed these fundamentals, you can explore cutting-edge supplements and create an environment that supports your anti-aging goals. Start with one or two changes today – your future self will thank you for taking action now rather than waiting for the “perfect” moment that never comes.

Saurabh Kumar is the founder of SaurabhOrbit.com, a hub for tech news, digital marketing insights, and expert blogging advice. With a deep passion for technology and digital strategies, Saurabh simplifies complex trends into actionable insights for readers looking to stay ahead in the digital world. My mission is to empower entrepreneurs, tech enthusiasts, and marketers with the latest tools and knowledge to thrive in the online space.



